Diabetes Awareness
for Colville Tribes
Prevent the onset of diabetes, and manage existing symptoms by making simple lifestyle changes.
(509) 634-2970 Monday-Thursday 7a-5:30p
Our Mission
Our mission is to provide the highest quality, culturally competent health education services to each community in a collaborative manner which promotes a safe and healthy environment. We focus on providing preventative education tools for people through advocacy of healthy lifestyles that honor mind, body and spirit.

Simple Lifestyle Changes
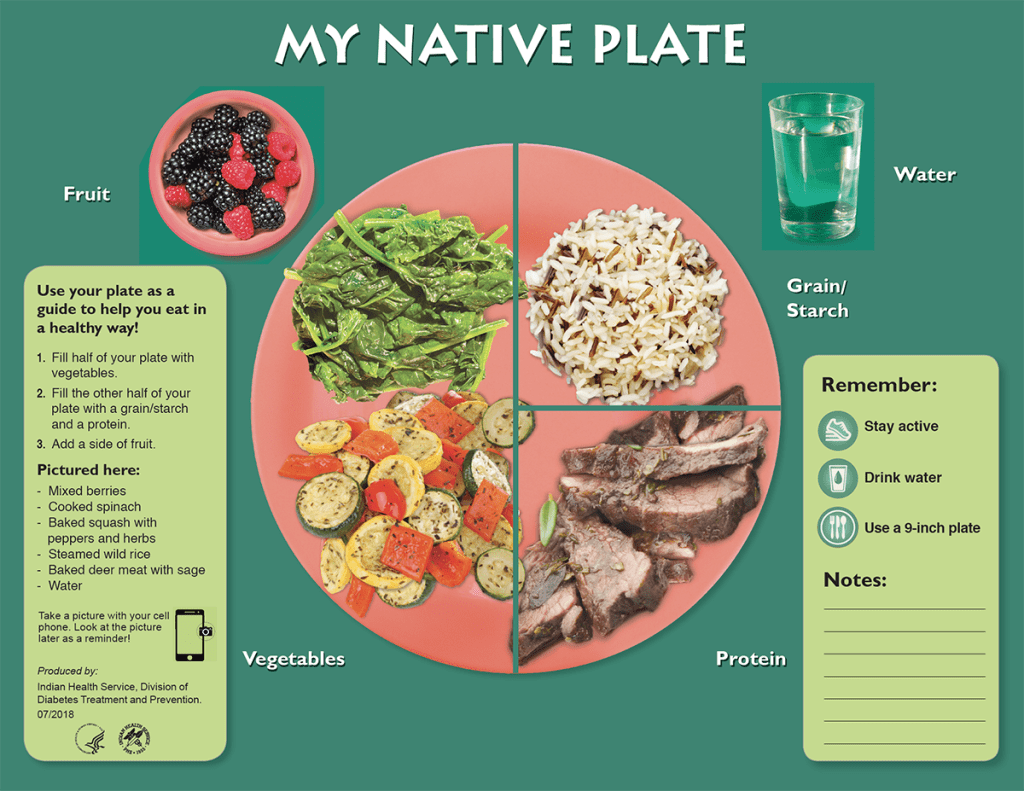
Healthy Eating
Get Moving
Create Routines
1 in 6
Native Americans have diabetes.
12
people every day undergo diabetes-related amputations.
7th
diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States.
2x
Native Americans are 2.2 times more likely to develop diabetes than other nationalities.
2/3
In about 2 out of 3 Native Americans with kidney failure, diabetes is the cause.
34.2 M
people in the United States have diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose from food get into your cells to be used for energy. Sometimes your body doesn’t make enough—or any—insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells.
Signs of type 2 diabetes can be severe, very mild or none at all, depending on how high blood sugars have become. Look for these signs:
- Increased thirst
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue (feeling very tired most of the time)
- Increased urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
A blood test to check your blood sugar will show if you have pre-diabetes or diabetes.
Pre-Diabetes
People with pre-diabetes are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
You can reduce the risk of getting diabetes and perhaps even return blood sugar levels to normal with a small amount of weight loss through healthy eating and increased physical activity.
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. Your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive.
Type 2 diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make or use insulin well. You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops in some women when they are pregnant. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born. However, if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you have a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is actually type 2 diabetes.
Over time, high blood glucose leads to problems such as:
- Heart Disease
- Stroke
- Kidney Disease
- Eye Problems
- Dental Disease
- Nerve Damage
- Foot Problems
You can take steps to lower your chances of developing these diabetes-related health problems.
- Being physically inactive
- Having a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes
- Having had the kind of diabetes which can happen during pregnancy
- Being overweight
- Your health care team (doctor, nurse, diabetes educator, dietitian, psychologist, fitness coach, social worker) can help.
They can help you create a physical activity and healthy eating plan that will work for you. They can also inform you of the medication used to treat diabetes. - Get help from others. Talk with your family and friends and ask for support.
Helpful Resources
Start Tracking
Track eating and exercise to create lifestyle changes.
Take the Quiz
Take the CDC Quiz to learn if you may be pre-diabetic.
Share Posters
Share on your social media to spread awareness.
Healthy Can Be Tasty
How To Manage Diabetes
Five Diet Tips for Diabetes